Descriptions
Intelligent RTP Local Switching (iRLS) function is a software application for helping the operators achieves significant saving in the transmission bandwidth between the core network and the rural/remote areas.
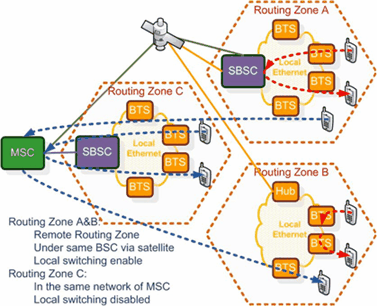
In standard GSM architecture, calls are routing to the MSC even if the calling and the called parties are in the same BSC zone. iRLS enables the system to route calls locally whenever the calling and called parties are in the same BSS zone; hence saving the backhaul transmission bandwidth. iRLS only controls the routing of the call traffic, the call signaling is still under the control of the host MSC.
In UltraWAVE system, the RLS, UES and VIM modules combine to provide the RTP local switching function. The RLS and UES modules are integrated in the MSS software. The installation doesn’t require extra hardware. The VIM is an independent software module. It should be installed in a separate Linux server. The UltraWAVE system can deploy up to ten VIMs to monitor up to 10240 local switching calls simultaneously. UltraWAVE system can spread local switching calls across two or more VIMs to reduce traffic congestion. Refer to the following introduction for more information of the VIM and UES modules.
Under certain circumstances the host MSC may insert voice announcement in a conversation. In this situation, iRLS must truncate the local switching on the conversation call to revert the payload switching back to normal so that the callers in the conversation can listen to the announcement. The function of Voice Insertion Monitor is monitoring the media payload activities from the host MSC. Once voice announcement is detected then the VIM will inform the iRLS to revert the ‘local switching’ back to ‘normal switching’ immediately.
|
If UltraWAVE system is connected to the PLMN via iPALIM then this function requires the PLMN MSC A-interface to support the UUI function. If the PLMN MSC A-interface doesn’t support UUI, then iRLS will use the User Equipment Simulator (UES) to create an IMSI - MSISDN table of all the online users to help the Dial Peers Pairing function to identify the originating and terminating parties of a call. When a new user location update to the IRO network the UES will use the IMSI of the new user to send a short message to capture his MSISDN. UES will then pass the IMSI - MSISDN information to the iPALIM. iPALIM manages the IMSI - MSISDN table and provides the information to the Dial Peers Pairing module for identifying the originating and terminating parties of a call.
|
See Also
Feature List
Feature |
Descriptions |
Capacity |
iRLS: •Up to 31 routing zones •Up to 100k BHCA VIM: •Monitor up to 1024 local switching calls per VIM system |
Voice Services |
Telephony Emergency call |
Data Services |
Data and Fax |
Supplementary Services |
Call forwarding: •Call forward unconditional (CFU) •Call forward on busy (CFB) •Call forward on not reply (CFNRy) •Call forward on not reachable (CFNRc) Call barring / Operator determined barring Notification of call barring Notification of call forwarding Password control Calling line identification presentation (CLIP) Calling line identification restriction (CLIR) Connected line identification presentation (COLP) Connected line identification restriction (COLR) Operator specific barring (OSB) |
Enhanced Services |
Prepaid Services |
Unique Services |
Intelligent RTP local switching Voice Insertion Monitoring (VIM) Dial peers pairing User Equipment Simulator (UES) function Invocation of local switching |
Redundancy |
Dual servers load sharing and active redundancy |
License Control |
Application flag: •Turn on/off iRLS •Turn on/off VIM |
Parameter |
Definition |
Range |
System |
-- |
-- |
•RLS Flag |
Enable or disable RTP Local Switching function. |
•Enable •Disable |
VIM Media Gateway |
-- |
Max 10 items |
•Administration State |
(Read Only) Control the operation of the managed MG. |
•Locked •Unlocked |
•IP |
IP address of VIM server. |
Dotted decimal format |
•Domain Name |
The domain name of the connected VIM. |
•vim-1234 |
•Switching Mode |
Switching mode of the VIM Media Gateway. Select MGCP as default. |
•MGCP •8ECP |
•Endpoint |
Method of MGCP endpoint description. Select Unstructured as default. |
•Structured •Unstructured •Unstructured Hex |
•Type |
(Read Only) Type of MG endpoint. |
VIM |
•Max Ports |
The total physical port number of the Media Gateway. |
-- |
•Max Channels |
The total channel number of the virtual MG. Applicable to virtual MG only. |
-- |
•Packetization Period |
The period over which encoded voice bits are collected for encapsulation in. |
•x20ms •x40ms •x60ms •x80ms |
•Codec Type |
(Read Only) Codec type of the Media Gateway. |
•AMR-12-2 |
•Audit Timer |
The time interval between sending AUEP message from MGC to MGW to check the trunk status. Unit is second. |
1 - 255 |
Routing Zone |
-- |
31 items |
•Site |
Determine each Routing Zone which configured in MSC Routing Zone table to Local or Remote. Refer to upper figure, the Routing Zone A and B are remote, while C is local. iRLS will not be invocated by the calls within local Routing Zone. |
•Remote •Local |
Return to
2.1.1.13