2.6 KiB
Introduction to OMC
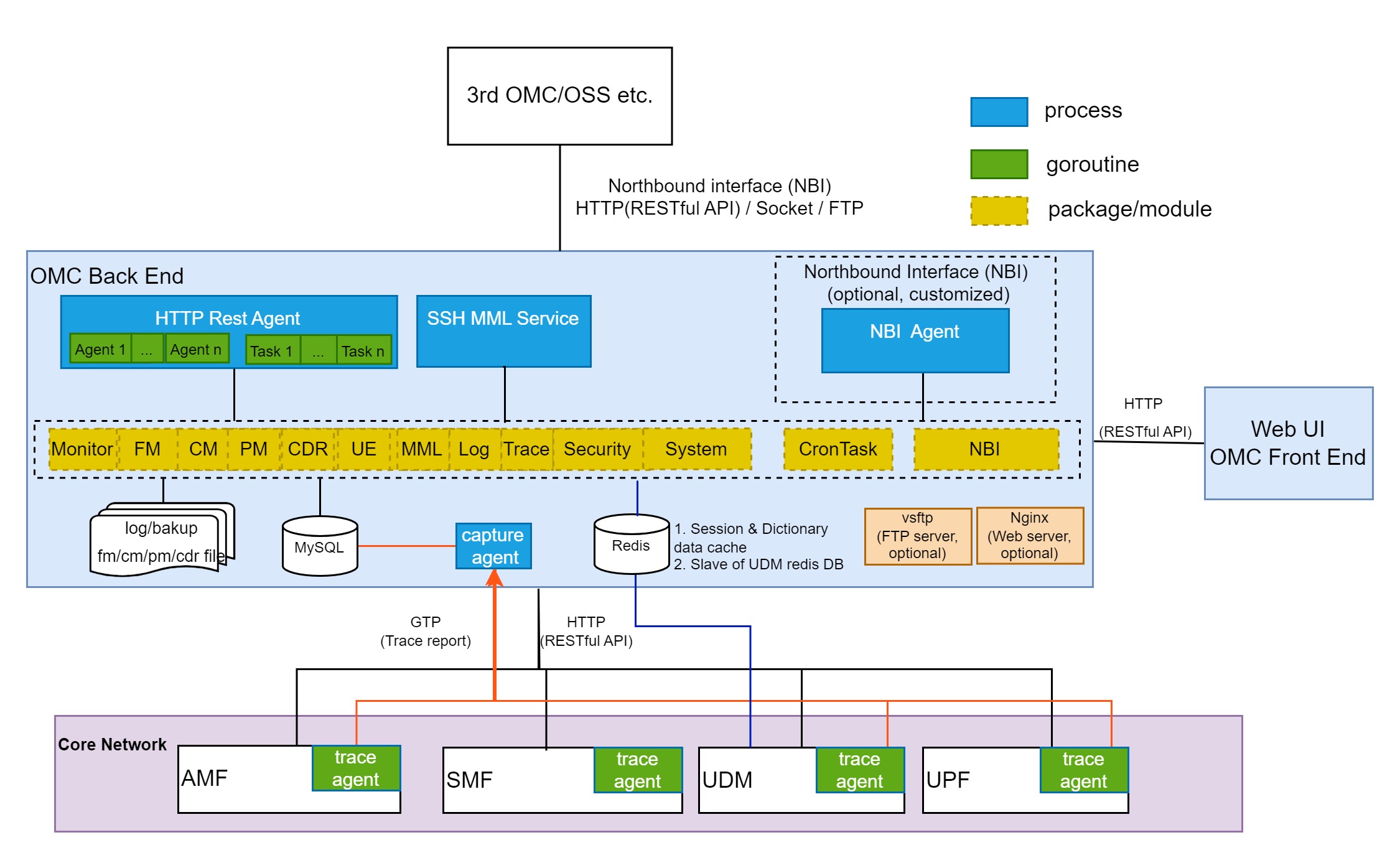
The Core Network OMC (Operation and Maintenance Center) is a central facility used by operators to manage and maintain core network equipment. It typically includes modules for network monitoring, fault management, performance management, configuration management, security management, and other functions to ensure the smooth operation and efficient maintenance of core network equipment. By monitoring and managing core network equipment, the OMC can quickly identify and resolve network faults in real-time, improve network performance, ensure network security, and enhance operational efficiency. The OMC plays a crucial role in the network operations and maintenance of operators, serving as a key element in ensuring stable network operation.
System Architecture
Platform
- Operating System: Linux
- Hardware Platform: X86/ARM64
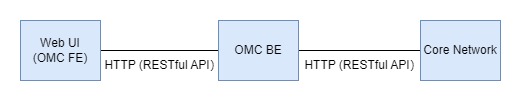
- Network Architecture: B/S mode
- Front-end Languages: HTML+CSS+JS (Vue3)
- Back-end Languages: Golang+MySQL/MariaDB+Redis, Nginx (optional)
Features
- Topology Management (Dashboard/State/Monitor): Dashboard, Network topology, System status, etc.
- Fault Management (FM): active alarms, historical alarms, etc.
- Configuration Management (CM): NE (Network Element) management, parameter configuration, etc.
- Performance Management (PM): subscription tasks for performance-related metrics, data reports, performance thresholds, etc.
- CDR/Event Managemet (CDR): IMS CDR, SMF CDR, AMF UE event.
- UE Management (UE): UDM Auth Data, UDM Subscriber, IMS Online Users, SMF UE Online Information, Radio Information, PCC Information, etc.
- Operation and Maintenance (MML): NE MML(Man Machine Language) operations, UDM (User Data Management) MML, OMC (Operation and Maintenance Center) MML, etc.
- Log Management (Log): operation logs, security logs, alarm logs, etc.
- Tracing Management (Trace): signaling tracking task creation, signaling analysis, signaling capture, etc.
- Security Management (Security): user management, role management, current online users, permission management, etc.
- System Management (System): menu management, dictionary management, system information, scheduling tasks, etc.
- Northbound Interface (NBI): optional and customized interfaces, northbound interface services, resource configuration data, performance statistics data, performance golden indicators, alarm reporting, 4A, etc.
Supported NEs
AMF, AUSF, UDM, SMF, UPF, PCF, NRF, NSSF, NEF, LMF, IMS, MME, N3IWF, SMSC, MOCNGW