Descriptions
Roaming is a general term in wireless telecommunications that refers to the extending of connectivity service in a location that is different from the home location where the service was registered. Roaming occurs when a subscriber of one wireless service provider uses the facilities of another wireless service provider. This second provider has no direct pre-existing financial or service agreement with this subscriber to send or receive information. A device will usually indicate when it is roaming.
The quintessential example of "roaming" is the case of cellular phones when a phone is in a location where its wireless service provider does not provide coverage (for example, another country). In some cases, roaming occurs in a phone's designated home area when it transmits via a different provider's tower (sometimes at a higher price). This is likely to occur when the service provider's signal is too weak or if the volume of callers is too high. In order for a mobile device to use a different carrier's service, the phone's service provider must have a roaming agreement with that carrier.
The functions of a location updating procedure are described below:
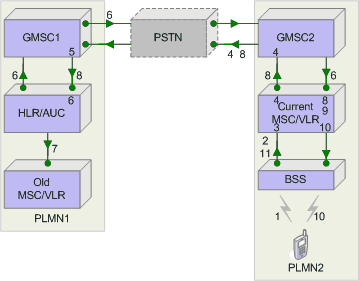
1.A mobile subscriber from the home PLMN1 activates his MS in PLMN2.
2.The MS requests the location updating procedure by sending the IMSI, the old LAI stored and the new LAI received, to the new VLR via its MSC.
3.The new VLR determines that the old LAI does not belong to its own area and therefore creates a database entry for the new mobile subscriber who is assigned the LMSI as an address.
4.By means of a global title translation on the IMSI, the new VLR obtains the signaling point code of GMSC2 and modifies the IMSI as described above. This GMSC2 in turn performs a global title translation which results in the addressing of GMSC1 in the home PLMN1.
5.By means of another global title translation on the modified IMSI, GMSC1 obtains the signaling point code of the subscriber's HLR. This allows the new VLR to establish a signaling path.
6.A successful subscription check at the HLR results in the mobile subscriber's registration in the new VLR of PLMN2. The HLR then supplies this VLR with all mobile subscriber data, including the zone code list belonging to the new VLR.
7.The HLR also requests the old VLR to cancel the mobile subscriber's data record by sending his IMSI.
8.The new VLR checks that the new location area belongs to a zone code from that list and informs the HLR on allowed roaming in the MSC area.
9.At this point, the regional subscription has been completely checked, and the new VLR carries out the authentication procedure using the received triple of the corresponding IMSI from the HLR.
10.Then, the new VLR initiates ciphering by sending the cipher-key to the MSC. The latter being requested to set the ciphering mode, passes it on to the BSS. The BSS starts the ciphering and deciphering process with the MS.
11.The MSC terminates the location update upon receiving a confirmation that the MS has stored the new LAI.
Implementation
1.Go to EMS >Configuration >NSS >SCCP.
2.Make sure the System ID at the upper right corner displays SCCP(MSS_Pub), click the
1.Click the GTT tab, and then click New at the bottom of the Globe Title Translate table.
2.In the GTT ID box, select an available number for the new entry, and then click the
3.In the GTT Option window, configure the following parameters to add GTT for remote HLR.
4.Click the
5.Repeat step 1 to 4 to add remote MSC and VLR.
|
1.On the GTT tab, click New at the bottom of the Globe Title Translate table.
2.In the GTT ID box, select an available number for the new entry, and then click the
3.In the GTT Option window, configure the following parameters to add GTT for inbound subscribers.
4.Click the
|
See Also
•Enable Country Specific Roaming Restriction (CSRR)
Return to
2.52